In the process of using low nitrogen burner, more solid carbon particles are easily generated in the flame, and the flame blackness is large. From the point of view of combustion, it seems not ideal to produce carbon particles, but most of these carbon particles can actually be burned out, and the radiation ability of the flame can be greatly increased, thus enhancing the heat transfer effect in the furnace, so the advantages outweigh the disadvantages. What are the combustion methods of gas combustion materials in low nitrogen burner? When the use conditions are the same and the burner structure is different, the mixing situation and flame length are also different. So what are the effects of gas fuel and air flow mode on flame length?
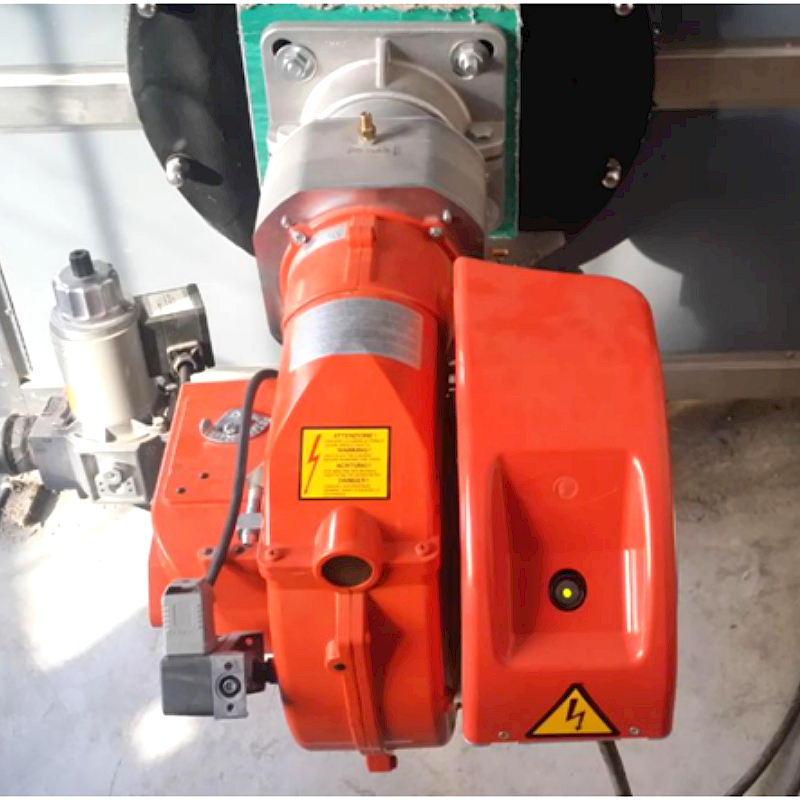
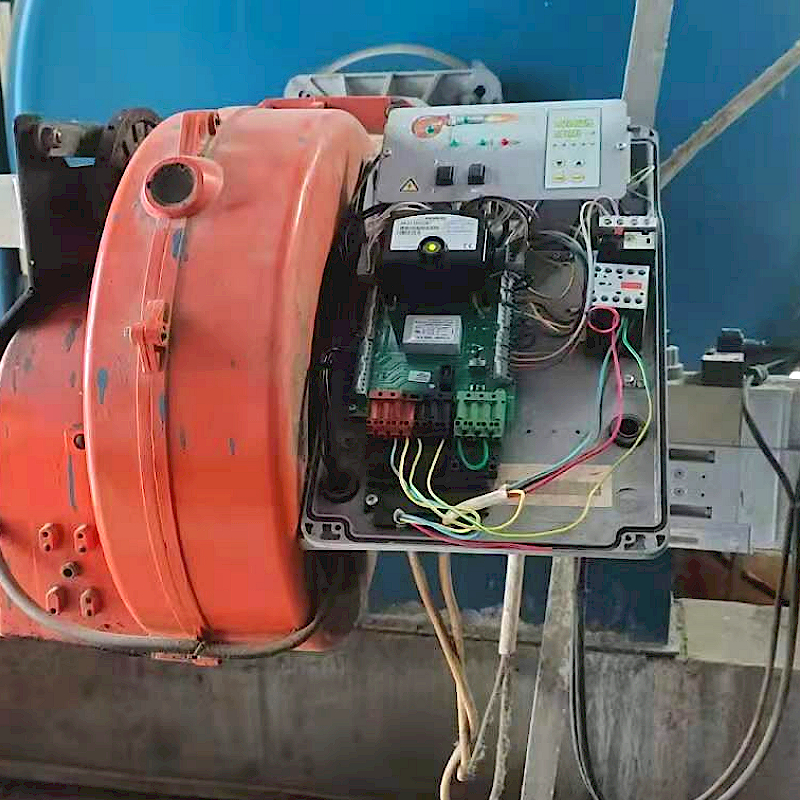
Commissioning site of 6-ton low-nitrogen burner
Combustion method of gas fuel in low nitrogen burner;
1. Flaming combustion
Flaming combustion means that the light body charge and air are not premixed before entering the combustion chamber, but are used to enter different combustion chambers, where they are mixed and burned, resulting in a long flame. It has a clear flame profile, also known as flame combustion. When the use conditions are the same and the burner structure is different, the mixing situation and flame length are also different.
The main way to improve the mixing conditions of gas and air is to strengthen combustion and organize flame, which can be achieved by changing the burner structure, such as forming an intersecting jet from the flow of gas and air to strengthen mechanical mixing. The use of flame combustion can allow air and gas to be preheated to a higher temperature without being limited by the ignition temperature, which is beneficial to obtain a higher combustion temperature with low calorific value gas and make full use of the waste heat surface of exhaust gas to save fuel.
Divide the gas into multiple streams to increase the contact area between gas and air; Increase the relative velocity of gas and air; Increasing the momentum ratio between gas and air and using rotating jet to enhance mixing. Because of the above characteristics, flame combustion has been widely used up to now, especially when the fuel consumption of the furnace is large or a long and bright flame is needed.
When gas fuel and air enter the furnace in parallel flow, the mixing conditions are poor and the flame is long. When gas fuel and air are sent into the furnace in two concentric jets, the mixing conditions are improved and the flame is slightly shorter. When gas fuel and air are sent into the furnace in the form of intersecting jets, and the outlet section of the burner is reduced, the outlet velocity can be increased, the mixing is better and the flame length is shorter.
2. Semi-flameless combustion
If only part of the air is mixed with gaseous fuel before combustion, it is called semi-flameless combustion. When semi-flameless combustion is adopted and gas fuel and air are mixed in the burner, the effect is better. The flame is short. It should be noted that when selecting a burner, it should not be determined only by the length of the flame, but also by whether the flame shape and its temperature distribution can meet the requirements of the process and whether the burner load adjustment range can meet the requirements of the furnace.
3. Flameless combustion
Flameless combustion means that gas fuel and air are mixed evenly in advance before entering the combustion chamber. Because its combustion rate only depends on the ignition and combustion reaction rate, it is faster than flame combustion, with short flame and no obvious flame profile. It belongs to power combustion mode. In order to achieve premixing, gas fuel is generally used as the injection medium and air is used as the injected medium.
It is not difficult to know that the length of flame is the symbol of diffusion and mixing process by summarizing the combustion methods of gas combustion materials in low nitrogen burner. The flame length indicates that the mixing and combustion progress quickly, and the air coefficient can be smaller. Short flame has good thermal performance, but it is not always better to use short flame. Different heating furnace types, heating objects and heating purposes often require different characteristics such as flame length. For example, a large furnace and a furnace requiring a long soaking zone want to release the combustion heat more evenly over a long distance, so a long flame is needed. Therefore, it should be noted that the selection of flame should not be based only on the speed of combustion, nor should it be simply evaluated on the length of flame.